RFID y UHF RFID explicados: una guía completa para logística, almacenamiento y gestión de activos
Introduction: When Traditional Management Meets Technological Limits
In traditional logistics and warehouse management, have you ever faced these situations?
Warehouse stocktaking requiring all-hands overtime, frequent missed or incorrect scans during manual barcode reading, spending hours locating a critical piece of equipment… These pain points silently erode organizational efficiency and profitability.
The emergence of RFID technology is quietly rewriting the rules of the game.
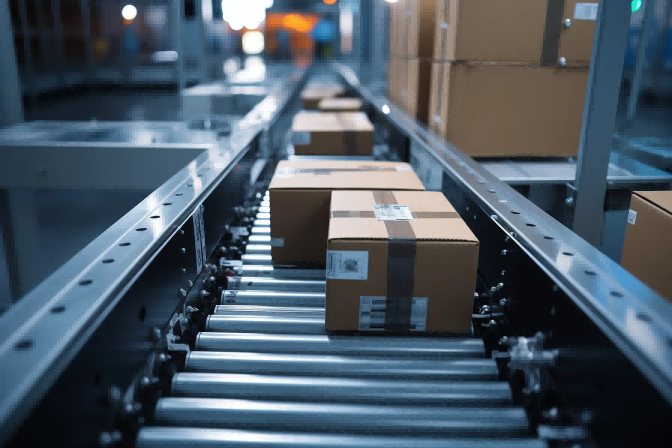

RFID Fundamentals — More Than Just an “Advanced Barcode”
1.1 What is RFID?
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) is a technology that uses radio waves to automatically identify objects and capture related data. Unlike barcodes that require direct line-of-sight, RFID tags can be read from several meters away without visual contact.
1.2 The Three Core Components:
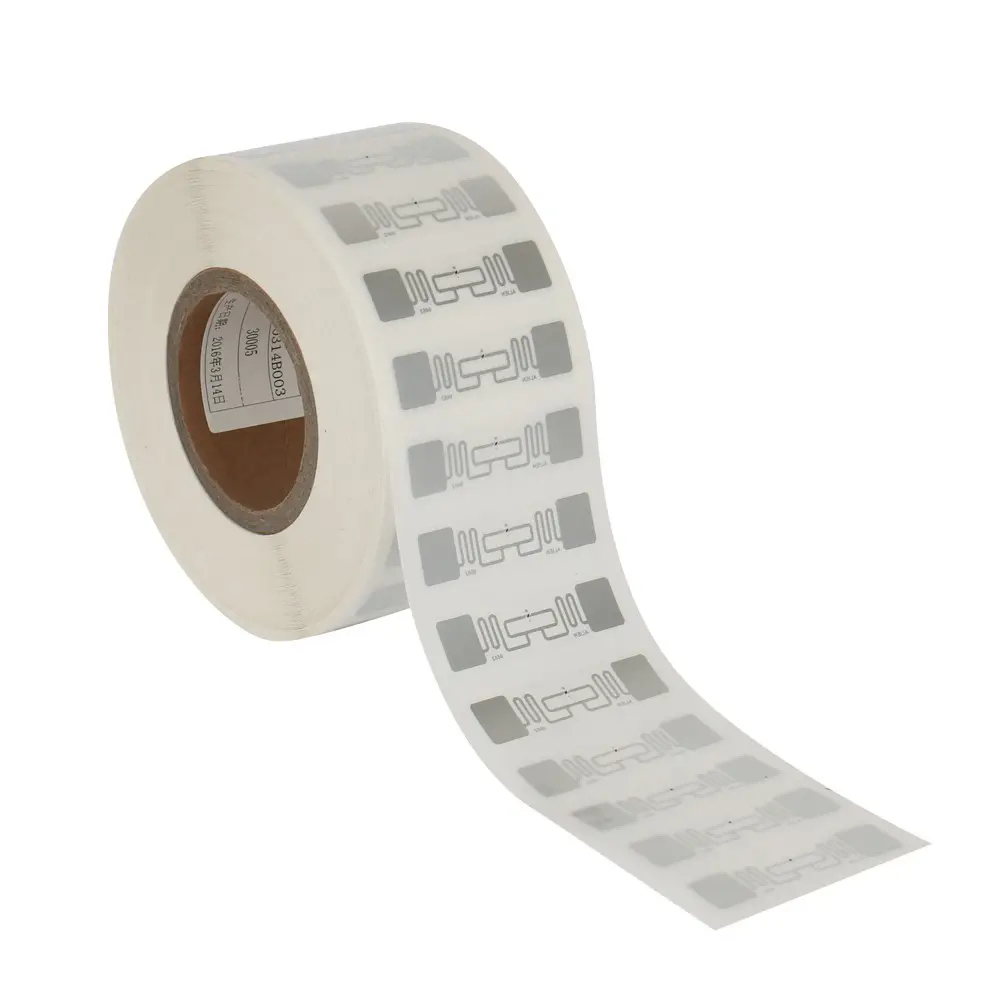
RFID Tags: Microchips integrated with an antenna, attached to items

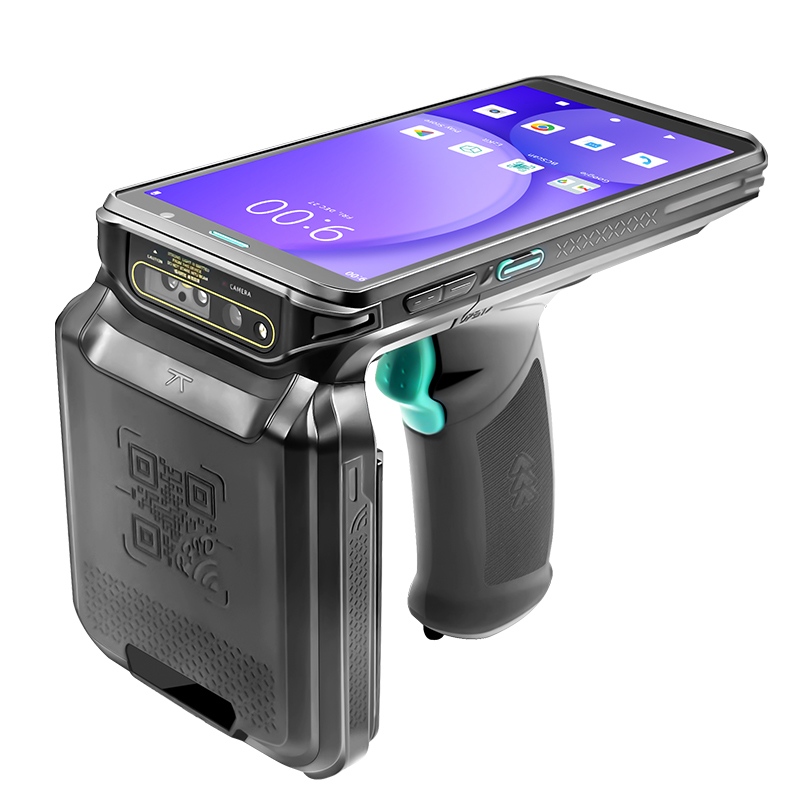
RFID Readers: Devices that transmit and receive radio signals to communicate with tags

Backend System: Software that processes, analyzes, and stores the captured data

UHF RFID — The Game Changer for Logistics and Warehousing
2.1 Key Advantages of UHF RFID
Operating in the 860–960 MHz frequency range, Ultra-High Frequency (UHF) RFID offers:
Longer read ranges — up to 10–15 meters
Bulk reading capability — hundreds of tags simultaneously
High-speed reading — 1,000+ tags per second
Better penetration — can read through non-metallic materials
2.2 Technology Comparison
| Parameter | Low-Frequency RFID | High-Frequency RFID | UHF RFID |
|---|---|---|---|
| Frequency Range | 125–134 kHz | 13.56 MHz | 860–960 MHz |
| Read Range | < 0.5 m | < 1.5 m | 1–15 m |
| Read Speed | Slow | Moderate | Very Fast (bulk read) |
| Interference Resistance | High | Moderate | Sensitive to metals/liquids |
| Typical Applications | Access control, animal tracking | Libraries, payment cards | Logistics, warehousing, retail |
The RFID Revolution in Logistics
3.1 End-to-End Visibility
From supplier to end-customer, every package, pallet, or container equipped with an RFID tag enables real-time tracking of:
In/out timestamps and responsible personnel
Transportation routes and transit points
Environmental conditions (with integrated sensors)
ETAs and exception alerts
3.2 Real-World Case: DHL
After deploying UHF RFID systems in its logistics centers, DHL achieved:
40% faster cargo processing
90% reduction in manual stocktake time
99.9% order accuracy
Annual savings of millions in operational costs

RFID Solutions for Smart Warehousing
4.1 Revolutionary Inventory Counting
Traditional manual count: 1 hour for 500 items
RFID count: 1,000 items in 1 minute
This leap in efficiency comes from RFID’s bulk-read capability. Staff simply walk through aisles with a handheld or vehicle-mounted reader, capturing data from hundreds of items in seconds.

4.2 Smart Shelving & Real-Time Inventory
RFID-enabled smart shelves can:
Automatically log item removal and replacement
Monitor stock levels in real time and trigger auto-replenishment
Prevent misplacement and optimize space utilization
Eliminate “lost stock” scenarios
ETIQUETAS CALIENTES
:
Sistema de inventario RFID para la eficiencia del almacén
RFID UHF frente a escaneo de códigos de barras para el seguimiento de activos
ROI de la implementación de RFID en la gestión de la cadena de suministro
Gestión de activos RFID para el seguimiento de equipos de fabricación
Integración de datos RFID con sistemas ERP
Hi! Click one of our members below to chat on